Let’s start by diving into the world of cannabis compounds. THCA and THC stand out as fascinating elements with distinct attributes. You see, THCA is the acidic form of THC which are found in raw cannabis plants – these are not the same. THCA won’t make you “high,” as THC is the compound responsible for it.
Understanding THC and THCA’s chemical structures, their effects on the endocannabinoid system, and their potential benefits will help consumers decide on how to use them. Starting with their chemistry, let’s explore the intricate details of cannabinoid compounds to differentiate THCA from THC.
Introduction: Unveiling the Mystery of THCA vs. THC

Background: The Role of Cannabis Compounds
Marijuana contains complex chemical compounds called cannabinoids. When consumed, it interacts with various cannabinoid receptors in the human’s endocannabinoid system to produce psychoactive properties or the feeling of getting “high.” Aside from this, the endocannabinoid system also process:
Mood
Appetite
Pain sensation
THCA or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the non-psychoactive substance that becomes THC or tetrahydrocannabinol. It exists abundantly in unheated cannabis plants and flowers. Upon heating, THCA undergoes a chemical reaction known as decarboxylation, converting it into THC.
This transformation is vital to the plant’s interaction with consumers, as THC binds with cannabinoid receptors. Understanding their roles is crucial for medicinal and recreational cannabis consumers, as well as navigating the laws surrounding cannabis consumption.
Understanding THC vs THCA: The Basics
One of the main difference between THCA and THC is their molecular structure. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the non-psychoactive cannabinoid acid naturally present in cannabis plants. It’s the biosynthetic precursor to THC, the substance responsible for the plant’s intoxicating effects to people.
While these two compounds share similar structure, the presence of an extra carboxylic acid group in THCA makes it non-intoxicating. Unlike THC, THCA doesn’t bind to two major cannabinoid receptors called CB1 and CB2. Because of this, THCA doesn’t create the “high” that users look for when consuming raw cannabis flower or plant.
THCA: The Non-Psychoactive Cannabinoid
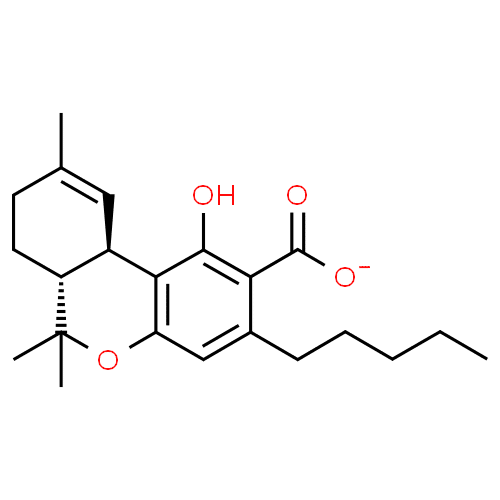
Chemical Structure and Functions of THCA
As we have already mentioned, THCA has an extra carboxylic acid group, responsible for its non-psychoactive property. This group is attached to a resorcinol ring, a common feature in cannabinoid acids, which plays a crucial role in the pharmacological diversity of cannabis.
THCA doesn’t fit well into the cannabinoid receptors due to its three-dimensional shape, thanks to the carboxyl group. This is why consuming THCA or raw cannabis will not get you high. However, THCA may just be beneficial if you’re looking for health benefits, which we’ll discuss later.
The Process: How the Cannabis Plant Produces THCA
Producing THCA is natural to the plant’s life cycle, which primarily occurs in the trichomes. These are the resin glands of the plant that are also responsible for producing aromatic oils or terpenes.
THCA synthesis begins when geranyl pyrophosphate and olivetolic acid combine through an enzymatic reaction. This process converts it into CBGA or cannabigerolic acid, which is then specifically synthesized into THCA by the enzyme THCA synthase.
This conversion starts as the cannabis plant matures along with proper light exposure and temperature. The amount of THCA produced will vary depending on different strains of cannabis, which can affect potency and therapeutic effects of the plant. Understanding this biosynthesis is important for consumers and cultivators, as it will influence the final concentration of THC in mature plants after the decarboxylation process.
Potential Benefits: Neuroprotective and Anti-inflammatory properties
According to research, THCA could have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. This makes it useful for inflammatory bowel diseases and neurodegenerative disorders. However, while THCA is believed to contribute to the plant’s self-defense mechanisms and overall health, its functions within the cannabis plant are not yet fully understood.
THCA may have psychoactive properties but it offers potential benefits. Because of this, researchers and medical professionals are drawn to it, showing how beneficial THCA can be in the medical industry. One of the most promising component of THCA is its neuroprotective properties.
Studies suggest that THCA can help protect brain cells from neurodegenerative damages like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. This creates an exciting news as it opens up possibilities of THCA being used as a therapeutic agent that can help treat these conditions. THCA also has potent anti-inflammatory properties. This can be beneficial for conditions like
Arthritis
Crohn’s disease
Multiple sclerosis
Unlike traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs, which can have harmful side effects to the human body, THCA offers a safer alternative to managing inflammation. These findings, although at the early stages, brings opportunities in developing new treatments for various health issues and conditions.
Legal Stance: Understanding Cannabis Laws around THCA
Now that we understood THCA’s nature and effects, it’s time to delve into the laws that govern this alluring medicinal plant.
The legality of cannabis is very complex and varies all over the world. When it comes to THCA, the legal status are up for debate since it doesn’t produce intoxicating effects – influencing its legal classification. In regions classifying THC as a controlled substance, THCA falls into a gray area as people can still convert it into THC.
However, some places have unique regulations that address cannabis, particularly with THC. In the US, the 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp which is cannabis that contains a THC concentration of less than 0.3% on a dry weight basis. As a result, THCA extracted from hemp could be considered legal at the federal level, provided it remains below the threshold of 0.3%. This is important for those who use cannabis as it will impact accessibility and use depending on the laws imposed in their local and federal government.
THC: Psychoactive Effects and More
Chemical Structure: Inside the Active THC Molecules
The THC molecule, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is the most popular cannabinoid due to its effects. Its chemical structure is similar to THCA, but with a critical distinction – the absence of the carboxylic acid group caused by heating. This small change has a profound impact on the molecule’s pharmacology. Due to THC’s structure, it easily binds to CB1 and CB2 receptors, particularly in the brain and nervous system.
Powerful Impact: How THC Produces the High
When THC binds to CB1 receptors, it triggers neurotransmitter releases leading to the well-known “high.” This binding alters the functions of these receptors which can lead to euphoria and altered sensory perception. These receptors are responsible for regulating:
Mood
Memory
Appetite
Pain
The reason THC can produce psychoactive effects is due to its lipid-soluble nature. This significantly affects its effectiveness as it allows the compound to easily cross our blood and brain to interact directly with our neural cells. This direct interaction can influence the release of dopamine hormones. These hormones, also neurotransmitters, regulate pleasure and reward in our brains, which then can contribute to the euphoric sensation.
Moreover, THC’s effects are dependent on the dosage used, the person’s tolerance to substance, and the presence of other cannabinoids and terpenes in the cannabis product. These factors can greatly improve or reduce the experience. With the right combination, it can lead to relaxation. However, others may experience anxiety or paranoia, an experience people wouldn’t want to be in.
Understanding how THC produces these effects is crucial for those who want to manage its impact, duration, and potency.
Therapeutic Applications: A Look Into Medical Marijuana
Aside from its psychoactive properties, THC is known for its medical potential. While it’s not as beneficial as THC, this still led to widespread use of medical marijuana among cannabis users and non-users.
Due to THC’s ability to alleviate symptoms of different conditions, thanks to its analgesic and antiemetic properties, more and more people support the use of marijuana for medical purposes. THC can be used to:
Provide relief from chronic pain, making it an effective alternative for patients who may not respond to traditional pain medications.
Stimulate appetite and reduce nausea, making it beneficial to individuals undergoing chemotherapy or those with AIDS.
Help patients with multiple sclerosis due to its muscle relaxant properties.
Treat neurological and mood disorders, like anxiety and PTSD.
However, medical marijuana is still a young field. We still need further studies to fully realize the effectiveness and safety of THC in various medical treatments. As research continues, THC can have more medical applications, further integrating it into medical practice and treatment. Also, since medical marijuana’s legalization varies, many countries require prescriptions or special licensing before anyone can use it. These two concerns go hand-in-hand in marijuana legalization and acceptance.
Legality: Navigating Cannabis Laws for THC
THC’s legality is more complex than THCA and varies significantly worldwide but it’s just as important. In many places, THC is classified as a controlled substance. However, more and more people are pushing for its legalization and decriminalization, especially for medical use. In the US, several states have already legalized marijuana for medical and even recreational use. However, it still remains illegal under federal law.
This contradicting laws often create confusion for consumers. So, it’s important to stay informed about the specific laws in your local jurisdiction, as it can significantly affect marijuana cultivation and consumption. Furthermore, the legality of marijuana is continues to evolve as more research backs up its benefits and as more people support its legality.
Medical and recreational marijuana may soon be widely accepted. But for now, anyone who wants to deal with cannabis must be aware of the complex local and federal regulations to ensure compliance and avoid legal consequences.
THCA vs. THC: A Comparative Analysis
| THCA | THC |
|---|---|
| Doesn’t get you high 😐 | Get’s you high 🫠 |
| Located in raw, unprocessed flower | Forms through the decarboxylation of THCA |
| Does not directly interact with brain’s cannabinoid receptors | Directly binds with brain’s cannabinoid receptors, inducing euphoria and altered perceptions |
| Conversion to THC requires decarboxylation (heat) | Found in cannabis that has been heated or aged |
| Offers potential therapeutic benefits without causing intoxication | Utilized for both recreational and medicinal purposes due to its effects |
Understanding the Chemical Reaction: The Decarboxylation Process
As we have mentioned earlier, decarboxylation is the chemical process that transforms THCA into THC, making it psychoactive. This process starts with releasing carbon dioxide by breaking the bonds of the carboxyl group from the THCA molecule through heat. You can do this by heating the cannabis during smoking, vaporizing, or cooking.
Decarboxylation can still happen at room temperature, however adding heat can accelerate this process. You may be thinking adding more heat would speed things up, but you’re wrong. Without proper control of temperature, the heat could degrade THC, making it less potent. If you want to use cannabis, it’s vital to understand how decarboxylation process works so that you can achieve your desired potency.
Availability: Purchasing Marijuana Products With Both Compounds
When it comes to purchasing marijuana, consumers now have a wide access to a variety of compounds. Also, the availability will vary on your local laws and regulations and the type of product available near you.
In countries legalizing the medical and recreational use of marijuana, you can easily find them in retail shows. They’re either offered as raw flowers, the THCA variant, or as processed products, the THC variant. If you prefer THCA for its benefits, you can also look for raw cannabis juices or tinctures. However, if you prefer THC, you may try edibles, oils, and concentrates.
Remember to inquire about the product’s levels of both THC and THCA to ensure you make an informed decision.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
Both THCA and THC interact with the endocannabinoid system. However, only the THC compound can induce a euphoric effect and THCA offers more health benefits. The choice will depend on your desired goals if you want to get “high” or treat various diseases. On the downside, THC is more well-known and research compared to THCA. This makes THCA very limited and may still be considered illegal in your country or state.
THC, on the other hand, is known for its strong psychoactive effects. This makes it useful for stress relief, creativity, and recreation. Additionally, THC has already established therapeutic applications in pain reduction and appetit stimulation.
However, THC can impair your cognitive functions and motor skills. This makes it unsuitable for some, especially those with mental health conditions. Balancing these factors is crucial in making your decisions.
Exploring Consumption Methods: THCA Extracts vs. Cannabis Flower
Aside from which compound you want to consume, you also need to know how to consume them properly. THCA can be consumed as tinctures, oils, or juices. This allows for precise dosage and offers a discreet consumption method. Cannabis flower, on the other hand, is typically consumed through smoking for its psychoactive effects.
Knowing the differences between THC and THCA will help you determine which compound to use depending on your goals and preferences.
Looking into the Future: Trends in the Cannabis Industry
As the cannabis industry evolves, it looks like more and more people will accept it. With more researchers studying the potentials of THCA and THC, it is likely to uncover more therapeutic benefits. This is also followed by advancements in cultivation and extraction techniques, enhancing the quality of various cannabis strains.
Even legalization movements are gaining momentum globally. This could result in more countries legalizing cannabis for medicinal or recreational use and increase market size and consumer access. Additionally, people are now looking for a more personalized experience from cannabis. By adjusting the product’s potency, it could offer tailored effects and health benefits. Technology also plays a huge role in enhancing consumer experience. From product selection to delivery, cannabis can now be consumed more conveniently.
As the world improves regulation, cannabis could become standardized, improving its quality control. This ensures consumers more safe and reliable products. Ultimately, cannabis usage and regulation shows a promising future not just with consumers but also for businesses.